Kafka Introduction
Introduction
Kafka is an event streaming platform, which provides following possible functionalities
publishandsubscribeeventsstoreevents indefinitelyprocessandanalyzeevents
Wait, but what is an event ?
An event is any meaning information that needs to be sent across network. Basically it has 3 main properties
- key
- value
- timestamp
Each event is a part of a stream, called a Topic. We can think of a topic a sequence of updates for a specific purpose. For example price updates for stocks. It is encoded commonly using AVRO format.
Uses
Lets dissect thes uses in detail -
- Publish and Subscribe Events
Basics of a PubSub pattern can be seen anywhere on internet. We will not go into detail into it.
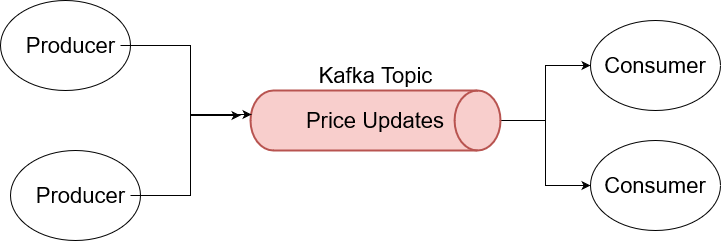
In Kafka world, publishers are called Prodcers and subscribers are called Consumers. Producers publish events on a Kafka topic and the same topic is subscribed by consumers.
Streams and KTables
| Streams | KTables |
|---|---|
| Provides immutable Data | Provides mutable data |
| Supports only inserts for new data | Supports insert, update and delete |
- Both are concepts of Kafka’s processing layer, which work on “raw” data in topics.
- Both can be partitioned and so it the processing on it.
- For streams, processing raw events in a topic for a partition is simple.
- For tables, to do aggregates, each partition may be associated with a light database. By default its RocksDB. It is stored within the application instance consuming the topic.
Kafka Topics
- Sequence of encoded events
- Defines a number of settings like Compression and data retention.
- They can be partitioned across different brokers
Kafka Brokers
- Machines that actually store and serve the data
- Has no idea about the content of the messages since its encoded.
Kafka Consumer group
- Bunch of consumers listening to a topic parallely.
- Can rebalance load between consumers within the group, when some of them fails or more are added.
- Operates within a Consumer group protocol
Kafka Stream Task
- Unit of processing parallelism
- One Stream Task is created for each partition in topic
- Stream task is distributed across app instances
Global Tables
- Provides data on global events.
- Cannot be partitioned.
Fault Tolerance
- Streams are fault tolearant since data is already stored in Kafka.
- Its a bit special for tables, since they store data on the application instance. They do it by sending the changes to a new Kafka topic. So just like a REDO log in Postgres, they can rebuild the table using the logs in case of any failure.
Scaling
- When scaling up or scaling down, kafka needs to transfer the data for Tables to new application using the changelog kafka topic.
Source -
- https://www.confluent.io/blog/kafka-streams-tables-part-1-event-streaming/
- https://www.confluent.io/blog/kafka-streams-tables-part-2-topics-partitions-and-storage-fundamentals/
- https://www.confluent.io/blog/kafka-streams-tables-part-3-event-processing-fundamentals/
- https://www.confluent.io/blog/kafka-streams-tables-part-4-elasticity-fault-tolerance-advanced-concepts/